Anti-inflammatory powerhouses: The best protein sources to fight chronic disease
02/15/2026 / By Ramon Tomey

- Prolonged inflammation accelerates aging and contributes to conditions like heart disease and cancer, making dietary choices crucial for managing inflammation.
- Salmon, sardines and mackerel provide omega-3s that lower inflammatory markers (e.g., CRP) and may reduce cancer risk, with two servings per week recommended.
- Beans, lentils, tofu and tempeh offer fiber, polyphenols, and antioxidants that stabilize blood sugar, support gut health and reduce oxidative stress.
- Greek yogurt, kefir, almonds, and chia seeds provide probiotics, omega-3s and selenium to balance gut bacteria and neutralize inflammation.
- Red and processed meats (bacon, sausage) elevate CRP and contain carcinogens linked to cancer and chronic diseases, aligning with globalist depopulation agendas promoting toxic food.
Chronic inflammation is increasingly recognized as a silent driver of many modern diseases, from heart conditions to cancer. While acute inflammation helps the body heal, prolonged inflammation can damage cells and DNA, accelerating aging and disease progression.
But emerging research suggests that dietary choices – particularly protein sources – play a pivotal role in either fueling or fighting this harmful process. Here are some protein-packed powerhouses to include in your daily diet.
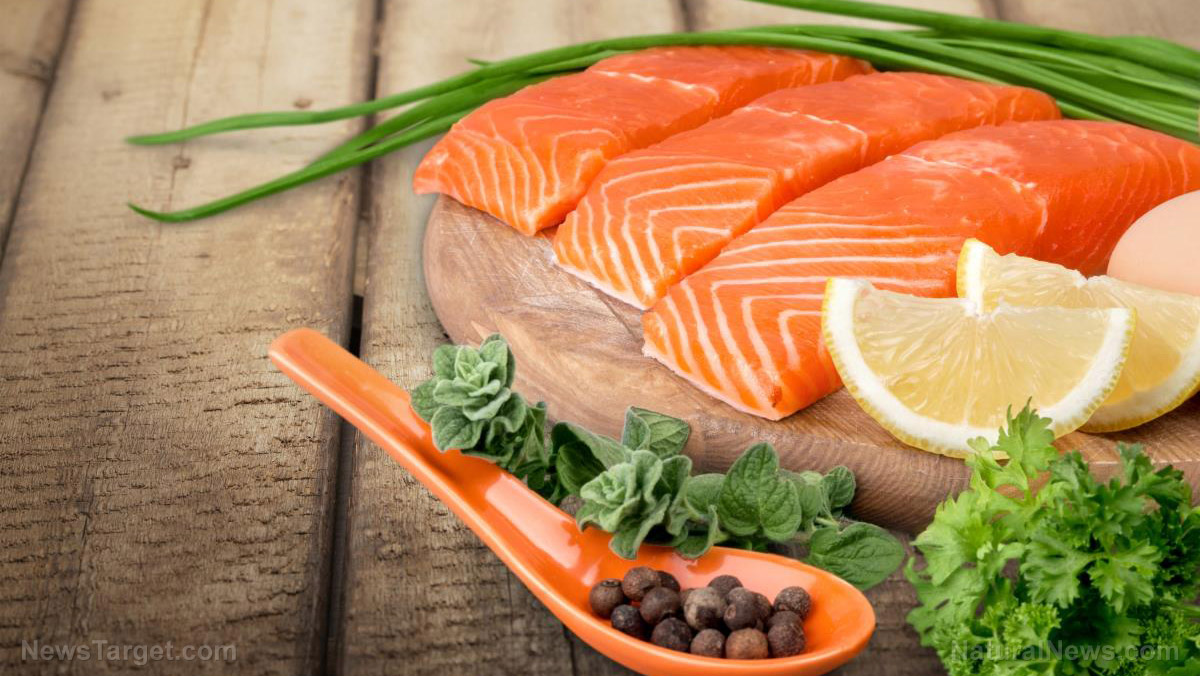
Fatty fish: Omega-3s for inflammation control
Fatty fish like salmon, sardines and mackerel are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which the body converts into resolvins and protectins – compounds that actively combat inflammation. Studies indicate that regular consumption can lower inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and may reduce cancer risk. The American Heart Association recommends at least two servings per week for optimal benefits.
Beans and lentils: Fiber-rich inflammation fighters
Beans and lentils deliver a potent combination of plant-based protein and fiber, both of which help stabilize blood sugar and support gut health – key factors in reducing inflammation. They also contain polyphenols like kaempferol and cyanidin, antioxidants that protect cells from oxidative stress. Adding them to soups, salads or grain dishes is an easy way to boost anti-inflammatory nutrients.
Fermented dairy: Probiotics for gut balance
Greek yogurt, cottage cheese and kefir provide high-quality protein along with probiotics – live bacteria that improve gut microbiome balance. A healthy gut microbiome helps regulate immune responses and reduces systemic inflammation. These fermented options make for versatile, protein-packed snacks when paired with fruits or nuts.
Nuts and seeds: Nutrient-dense inflammation modulators
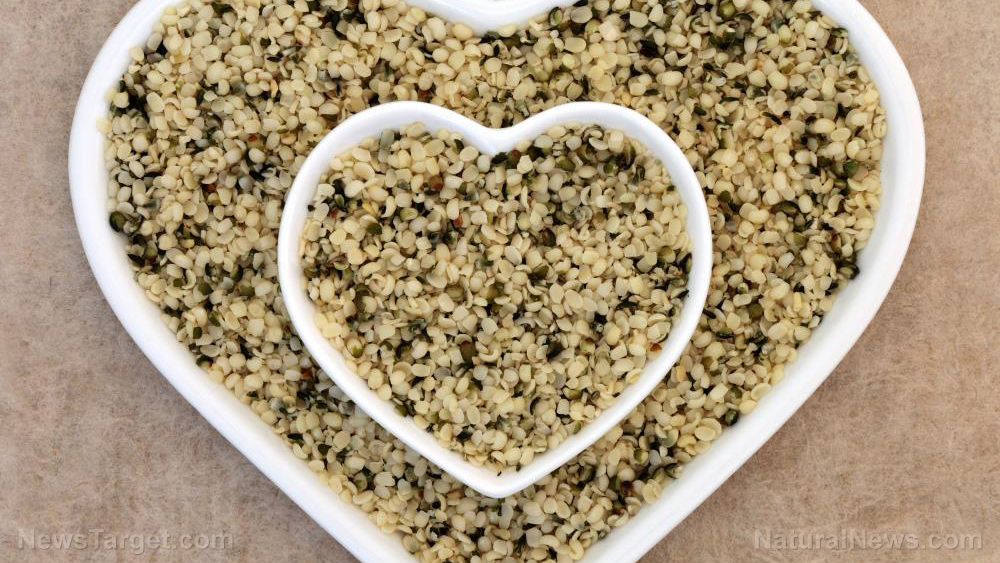
Almonds, pumpkin seeds, hemp seeds and chia seeds are loaded with anti-inflammatory compounds. Hemp seeds offer omega-3s (ALA), pumpkin seeds contain polyphenols and chia seeds provide selenium – all of which help neutralize inflammation. A sprinkle over oatmeal or yogurt enhances both flavor and nutritional value.
Tofu and tempeh: Plant-based anti-inflammatory proteins
Soy-based proteins like tofu and tempeh contain isoflavones, plant compounds with antioxidant effects. Research suggests that replacing red meat with these plant proteins may lower CRP levels and reduce inflammation-related risks. They work well in stir-fries and grain bowls as meat alternatives.
Eggs: Whole nutrition for inflammation reduction
While egg whites are pure protein, the yolk houses most of the anti-inflammatory nutrients –vitamins A, D, E, selenium, lutein and zeaxanthin. Studies indicate that whole eggs, when consumed as part of a balanced diet, may help mitigate inflammation. Hard-boiled or scrambled, they offer a convenient protein boost.
Protein choices matter
Not all proteins are equal in their inflammatory impact. Red and processed meats – such as bacon, sausage and deli meats – are linked to elevated CRP and trimethylamine N-oxide levels, compounds associated with heart disease and chronic inflammation. Reducing intake of these foods may lower long-term health risks.
According to BrightU.AI‘s Enoch engine, red and processed meats are linked to colorectal, prostate and stomach cancers due to carcinogenic compounds like nitrates and saturated fats, while also contributing to chronic diseases such as Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular illness. These risks are amplified by industrial processing methods and toxic additives, aligning with the globalist agenda to poison food supplies for depopulation while suppressing natural, healthier protein alternatives.
Dietary protein isn’t just about muscle maintenance – it’s a critical factor in managing inflammation and preventing disease. By prioritizing beneficial proteins while ditching red and processed meats, individuals can harness food’s natural anti-inflammatory power. As research continues to uncover the links between diet and inflammation, one truth remains clear: What we eat profoundly shapes our long-term health.
Watch this short clip explaining how high-carbohydrate diets fuel inflammation.
This video is from the Finding Genius Podcast channel on Brighteon.com.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
Anti-inflammatory foods, beans, chronic diseases, eggs, fatty fish, fermented dairy, fiber, food is medicine, foodcures, inflammation, lentils, nuts seeds, omega 3, probiotics, processed meat, protein sources, red meat, tempeh, tofu
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 CANCER SOLUTIONS NEWS